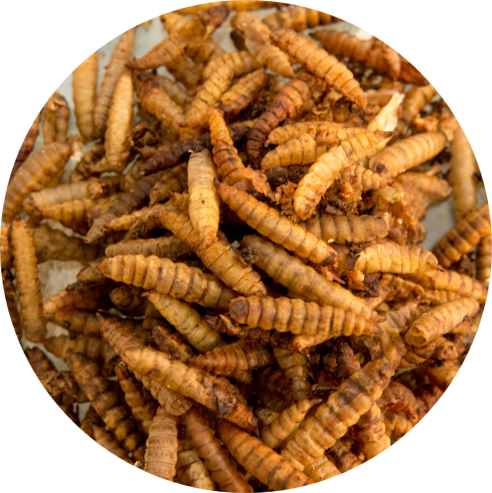
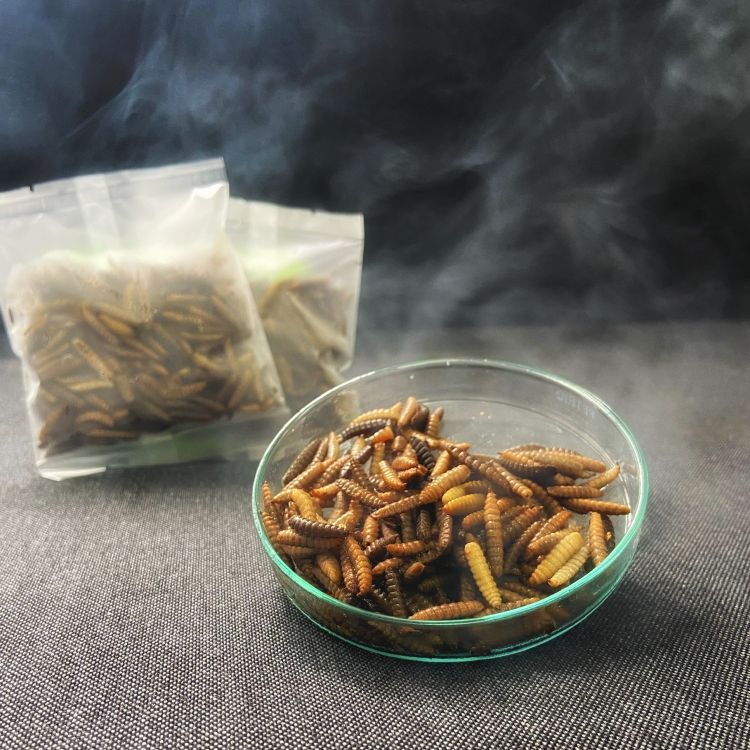
Eubio-BASE
The prophylactic addition of chemical antibiotics can reduce diseases and enhance growth efficiency in livestock and aquaculture animals, but it can also lead to drug residues and antibiotic-resistant pathogens, causing food safety and public health issues. Numerous domestic and international reports indicate a high proportion of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and widespread antibiotic resistance on farms. More importantly, antibiotic-resistant pathogens and antibiotic resistance can be transmitted from animals to humans, and further amplified through human-to-human transmission, posing public health and health problems.
The future trend in farming focuses on food safety (prohibition of chemical antibiotics) and environmentally friendly practices (aiming at reducing emissions, reuse, and recycling). Therefore, the use of antibiotic substitutes to replace antibiotics (antibiotic-free farming) in livestock farming is becoming a global trend. Bidens pilosa, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is distributed in temperate to tropical regions. Bidens pilosa is used as food and is promoted as a staple by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Africa, and is listed as food by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan. It is also a common herb, used to treat protozoal and bacterial infections, immune regulation, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, and 43 other functions. Bidens pilosa has also been proven to reduce diarrhea in pigs, with some mechanisms involving the regulation of microbiota.
The future trend in farming focuses on food safety (prohibition of chemical antibiotics) and environmentally friendly practices (aiming at reducing emissions, reuse, and recycling). Therefore, the use of antibiotic substitutes to replace antibiotics (antibiotic-free farming) in livestock farming is becoming a global trend. Bidens pilosa, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is distributed in temperate to tropical regions. Bidens pilosa is used as food and is promoted as a staple by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Africa, and is listed as food by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan. It is also a common herb, used to treat protozoal and bacterial infections, immune regulation, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, and 43 other functions. Bidens pilosa has also been proven to reduce diarrhea in pigs, with some mechanisms involving the regulation of microbiota.
- Company NameCHINA CHEMICAL & PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY
The prophylactic addition of chemical antibiotics can reduce diseases and enhance growth efficiency in livestock and aquaculture animals, but it can also lead to drug residues and antibiotic-resistant pathogens, causing food safety and public health issues. Numerous domestic and international reports indicate a high proportion of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and widespread antibiotic resistance on farms. More importantly, antibiotic-resistant pathogens and antibiotic resistance can be transmitted from animals to humans, and further amplified through human-to-human transmission, posing public health and health problems.
The future trend in farming focuses on food safety (prohibition of chemical antibiotics) and environmentally friendly practices (aiming at reducing emissions, reuse, and recycling). Therefore, the use of antibiotic substitutes to replace antibiotics (antibiotic-free farming) in livestock farming is becoming a global trend. Bidens pilosa, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is distributed in temperate to tropical regions. Bidens pilosa is used as food and is promoted as a staple by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Africa, and is listed as food by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan. It is also a common herb, used to treat protozoal and bacterial infections, immune regulation, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, and 43 other functions. Bidens pilosa has also been proven to reduce diarrhea in pigs, with some mechanisms involving the regulation of microbiota.
The future trend in farming focuses on food safety (prohibition of chemical antibiotics) and environmentally friendly practices (aiming at reducing emissions, reuse, and recycling). Therefore, the use of antibiotic substitutes to replace antibiotics (antibiotic-free farming) in livestock farming is becoming a global trend. Bidens pilosa, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is distributed in temperate to tropical regions. Bidens pilosa is used as food and is promoted as a staple by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Africa, and is listed as food by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan. It is also a common herb, used to treat protozoal and bacterial infections, immune regulation, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, and 43 other functions. Bidens pilosa has also been proven to reduce diarrhea in pigs, with some mechanisms involving the regulation of microbiota.










__24G16nrEmc.png)








